High temperatures may be used or low temperatures.
Ceramic oxidation fire definition.
In this process ceramics heated at a certain temperature pull oxygen from the kiln chamber and this oxygen get combined with carbonaceous materials present in the ceramic body and thereby oxidize the ceramic materials.
Oxidation reduction salt wood raku oxidation firing is typically done in an electric kiln but can also be done in a gas kiln.
Oxidation firing allow very bright rich colors.
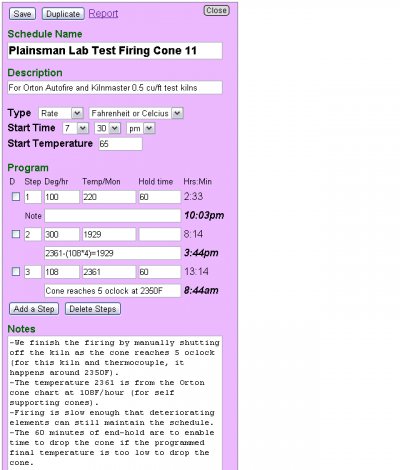
Oxidation and reduction in terms of firing schedules.
Reduction vs oxidation firing.
There are many ways to fire your clay.
Oxygen is free to interact with the glazes when firing.
With fuel burning kilns however care must be taken to ensure that the kiln does not go into reduction until the latter part of the firing usually the last half hour to the last hour and a half.
This is the clean burning efficient blue flame which is why easy temperature gains are synonymous with oxidation atmospheres.
Fire is an oxidation process that happens very fast so that light heat and sound are released often with enough force and majesty to justify the ancients reverence the sudden release of energy causes temperatures to rise sometimes by thousands of degrees.
Reversing the equation ethanal can be reduced by adding hydrogen to it to.
Oxidation firing definition oxidation firing is a technique used to oxidise ceramic materials.
Many people fire their gas kilns up in oxidation but at two places in the ramp e g.
Electric kilns are naturally in an oxidation or neutral atmosphere.
According to this definition oxidation is the loss of hydrogen while reduction is the gain of hydrogen.
With access to enough oxygen to efficiently burn your fuel you are almost exclusively producing water vapor and co2 which will cause oxidation of your ceramic surfaces.
The difference between oxidation and reduction firing.
The defining difference between a fire and your half eaten apple is speed.
In fact because almost all natural clays contain iron reduction firing normally gives completely different clay surface effects than oxidation.
Cone 06 10 they reduce the kiln for a period for body and glaze reductions.
For example according to this definition when ethanol is oxidized into ethanal.
Ch 3 ch 2 oh ch 3 cho ethanol is considered oxidized because it loses hydrogen.